Sample preparation
Liquor (0.5ml) were subjected to lipid extraction procedure in water-chloroform-methanol mixture (Folch procedure) followed by acid methanolysis of dry lipid residue in 0,4ml 1N HCl / methanol by heating to 80oC for 1hr. Phospholipid fatty acid methyl esters (FAME), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) hydroxy FAME were formed as a result and extracted with hexane. The hexane fraction were dried, and dry residue was silylated in 20mkl N,O-bis-trimethylsilyl-trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) by heating at 80 oC for 15min.
Whole blood (0.05 ml) were dried with equal quantity of methanol at 80OC and methanolysed in 0,4ml 1N HCl / methanol by heating to 80oC for 1hr. Fatty acid methyl and trimethylsilyl derivatization procedure was the same as liquor case.
Gas chromatography - mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis.
Measurements were performed on a Shimadzu QP-2000 system equipped with a cross-linked methyl silicone capillary column (Ultra-1). Analysis of fatty acids was done at the oven temperature was started 120OC and then programmed to 320OC at 5OC/min. 1mkl of derivatized sample were injected to gas chromatograph at 2800C. Fatty acids and other lipid components after separation in GC column were ionized by electron impact and analyzed in the selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode using appropriate ions for thirty four substances distributed in five separate ion groups throughout analytical range from decanoic acid to heaviest cholesterol metabolites. For instance, ion 87 was used for nonhydroxy and ion 175 for hydroxy FA. Each substance was confirmed by another specific ion, molecular or fragmentous, which is characteristic in mass spectrum. Another confirmations were achieved by measuring the specific retention times and ratio of chromatographic peak areas for selected ions of single substance. The analysis of lipid moiety by GC-MS-SIM technique provides a convenient way of obtaining quantitative data in spite of surpassing background caused by blood cells components. This is because the strongest ions of blood cells were not included in SIM and time program. Known quantity of CD3- tridecanoate was added as internal standard.
Example 1.
Gas Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry investigation microbial markers in
liquor. Sample LT-064. Patient M.A.
Fungal meningitis.
Fatty acid concentrations were considered in balance equations with partial include of single micro-organisms proposed as mixt infection members. Computerised solution appears to be effective in discovery of genera-species composition of symbiotic and invasive microflora and follow-up infection and disbiosis in body fluids with their 104 background lipid prevalence.
The resulting virtual concentration of micro-organisms in locus's, wich have contact with liquor is as follows:
|
No. |
Genera, species |
Sample content* |
Normal level** |
|
1 |
Clostridium perfringens |
123 |
10 |
|
2 |
Bacteroides fragilis |
0 |
2 |
|
3 |
Bacillus cereus |
1838 |
83 |
|
4 |
Staphylococcus haemolyticus |
0 |
13 |
|
5 |
Peptostreptococcus anaerobius |
5289 |
19 |
|
6 |
Propionibacterium |
243 |
71 |
|
7 |
Chlamidia trachomatis |
0 |
1 |
|
8 |
Enterococcus |
0 |
50 |
|
9 |
Enterobacteriaceae |
1011 |
56 |
|
10 |
Fusobacterium/Haemophylus |
0 |
21 |
|
11 |
Staphylococcus epidermidis |
2296 |
125 |
|
12 |
Neisseria/Moraxella |
0 |
0 |
|
13 |
Mycobacteria (TSA) |
0 |
114 |
|
14 |
Candida albicans |
860 |
136 |
|
15 |
Acinetobacter |
0 |
8 |
|
16 |
Bacillus (Streptomyces) |
3599 |
1800 |
|
17 |
Prevotela melaninogenica |
0 |
0 |
|
18 |
Corinebacterium |
0 |
0 |
|
19 |
Pseudomonas |
0 |
96 |
|
20 |
Flavobacterium |
0 |
0 |
|
21 |
Enterobacteriaceae (Serratia) |
0 |
863 |
|
22 |
Klebsiella |
0 |
397 |
|
23 |
Streptococcus |
0 |
0 |
|
24 |
Eubacterium |
0 |
526 |
|
25 |
Brucella, Francisella |
1801 |
0 |
|
26 |
Streptococcus pneumonia |
0 |
27 |
|
27 |
P.aeruginosa |
0 |
84 |
|
28 |
Diphteroids |
0 |
512 |
|
29 |
Cholestendiol (herpes) |
0,0 |
0 |
|
30 |
Virus 366/382 |
7 |
0,3 |
|
31 |
Treponema |
0 |
0,21 |
|
32 |
Ergosterol (fungi) |
0 |
0 |
|
33 |
Brucella, Francisella |
2630 |
0 |
*- calculated relative units which proportional to cells number
**- statistical level for blood in donor was taken as norm
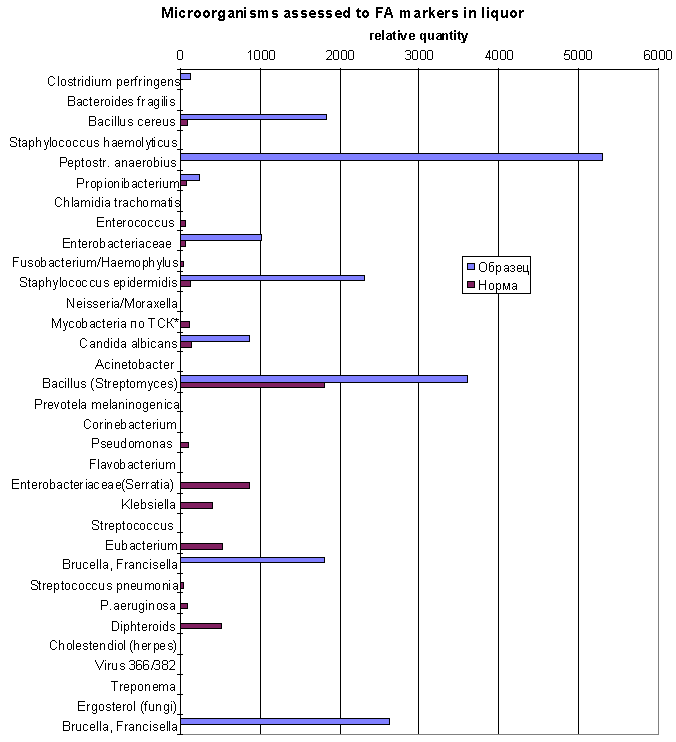
The same data in diagram form:
Brown sticks - norm, blue sticks - patient

The content of Candida albicans marker (17:1, heptadecenoic acid) overestimate normal level substantially. As well as markes of Clostridium perfringens (10h18, 10-hydroxystearic acid), members of Enterobacteriaceae family (cyclo-heptadecanoic acid), Peptostreptococcus anaerobius (prevalent one) also Staphylococcus epidermidis and Bacillus are in excess of norm.
Cholesterol metabolites referred to viruses (item 30) were discovered.
The interesting finding are Francisella (Brucella) double marker - hydroxyhexadecanoic and hydroxyoctadecanoic acids. We choose Francisella filomiragia because of seven cases (Medline search results) confirmed this microbe as meningitis agent. More of it, F.filomiragia was found in CSF by CDC staff collaborators and confirmed by GC FAME's profile ( D.G.Hollis, ..., C.W.Moss, et al., J.Clin.Microbiol. 27(7), 1601-08, 1989).
Microbial markers were analyzed in blood of the same patient, and calculated microorganisms presented in the next table:
Gas Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry investigation the composition of microbial
lipid markers in blood
Sample NT-064. Patient A.M.
Fungal meningitis.
|
¹ |
Genera, species |
Sample content* |
Normal level** |
|
1 |
Clostridium perfringens |
23 |
10 |
|
2 |
Bacteroides fragilis |
0 |
2 |
|
3 |
Bacillus cereus |
286 |
83 |
|
4 |
Staphylococcus haemolyticus |
30 |
13 |
|
5 |
Peptostr. anaerobius |
368 |
19 |
|
6 |
Propionibacterium |
82 |
71 |
|
7 |
Chlamidia trachomatis |
0 |
1 |
|
8 |
Enterococcus |
357 |
50 |
|
9 |
Enterobacteriaceae |
614 |
56 |
|
10 |
Fusobacterium/Haemophylus |
0 |
21 |
|
11 |
Staphylococcus epidermidis |
0 |
125 |
|
12 |
Neisseria/Moraxella |
0 |
0 |
|
13 |
Mycobacteria (TSA) |
0 |
114 |
|
14 |
Candida albicans |
1234 |
136 |
|
15 |
Acinetobacter |
0 |
8 |
|
16 |
Bacillus (Streptomyces) |
3614 |
1800 |
|
17 |
Prevotela melaninogenica |
0 |
0 |
|
18 |
Corinebacterium |
0 |
0 |
|
19 |
Pseudomonas |
0 |
96 |
|
20 |
Flavobacterium |
0 |
0 |
|
21 |
Enterobacteriaceae(Serratia) |
0 |
863 |
|
22 |
Klebsiella |
721 |
397 |
|
23 |
Streptococcus |
0 |
0 |
|
24 |
Eubacterium |
0 |
526 |
|
25 |
Bacteroides urealyticum |
231 |
816 |
|
26 |
Streptococcus pneumonia |
0 |
27 |
|
27 |
P.aeruginosa |
0 |
84 |
|
28 |
Diphteroids |
108 |
512 |
|
29 |
Cholestendiol (herpes) |
1,7 |
0 |
|
30 |
Virus 366/382 |
2 |
0,3 |
|
31 |
Treponema |
0 |
0,21 |
|
32 |
Ergosterol (fungi) |
0 |
0 |
|
33 |
Helicobacter pylory |
310 |
369 |
The same data in diagram form:
Brown sticks - norm, blue sticks - patient
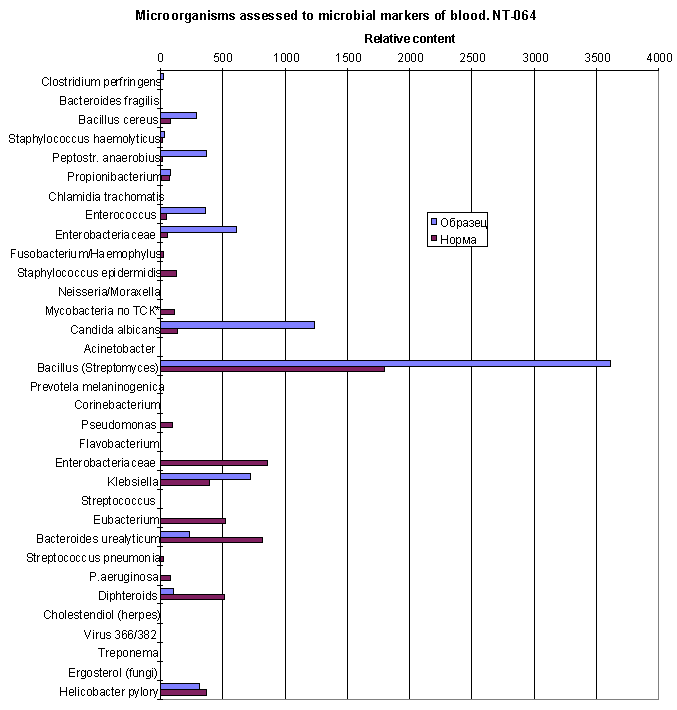
There are Candida albicans (main microbe), bacteria of Enterobacteriaceae family,
Enterococcus, Clostridium perfringens, anaerobic Peptostreptococcus anaerobius,
and member of Bacillus which markers exceeds the normal level in blood of healthy
people. Herpes virus cholestendiol is detectable.
The data does not mean, this bacteria are present in blood.
This microorganisms could be localised in various organs of human body, not really
in blood.
They come through in blood as a products of phagocytosis in that organs, and treated
in blood stream like other exogenous particles and substances.
Most of them come from liquor region. That ones which markers simultaneously appear
in liquor. But Enterococcus and Klebsiella originate from another part of body
because of their absence in liquor.
Example 2.
Gas Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry investigation microbial markers in
liquor. Sample LT-065. Patient B.
Bacterial and Fungal meningitis/encephalitis.
Measurements before and after treating.
1. Before treating
|
¹ |
Genera, species |
Sample content* |
Normal level** |
|
1 |
Clostridium perfringens |
59 |
10 |
|
2 |
Bacteroides fragilis |
0 |
2 |
|
3 |
Bacillus cereus |
861 |
83 |
|
4 |
Staphylococcus haemolyticus |
62 |
13 |
|
5 |
Peptostr. anaerobius |
1830 |
19 |
|
6 |
Propionibacterium |
642 |
71 |
|
7 |
Chlamidia trachomatis |
0 |
1 |
|
8 |
Enterococcus |
123 |
50 |
|
9 |
Enterobacteriaceae |
0 |
56 |
|
10 |
Fusobacterium/Haemophylus |
111 |
21 |
|
11 |
Staphylococcus epidermidis |
2238 |
125 |
|
12 |
Neisseria/Moraxella |
0 |
0 |
|
13 |
Mycobacteria (TSA) |
49 |
114 |
|
14 |
Candida albicans |
817 |
136 |
|
15 |
Acinetobacter |
0 |
8 |
|
16 |
Bacillus (Streptomyces) |
4564 |
1800 |
|
17 |
Prevotela melaninogenica |
0 |
0 |
|
18 |
Corinebacterium |
0 |
0 |
|
19 |
Pseudomonas |
0 |
96 |
|
20 |
Flavobacterium |
861 |
0 |
|
21 |
Enterobacteriaceae(Serratia) |
3126 |
863 |
|
22 |
Klebsiella |
984 |
397 |
|
23 |
Streptococcus |
0 |
0 |
|
24 |
Eubacterium |
0 |
526 |
|
25 |
Bacteroides urealyticum |
1394 |
816 |
|
26 |
Streptococcus pneumonia |
763 |
27 |
|
27 |
P.aeruginosa |
0 |
84 |
|
28 |
Diphteroids |
295 |
512 |
|
29 |
Cholestendiol (herpes) |
0,0 |
0 |
|
30 |
Virus 366/382 |
0 |
0,3 |
|
31 |
Treponema |
0 |
0,21 |
|
32 |
Ergosterol (fungi) |
0 |
0 |
|
33 |
Helicobacter, Francisella |
1441 |
369 |
The same data in diagram form:
Brown sticks - norm, blue sticks - patient
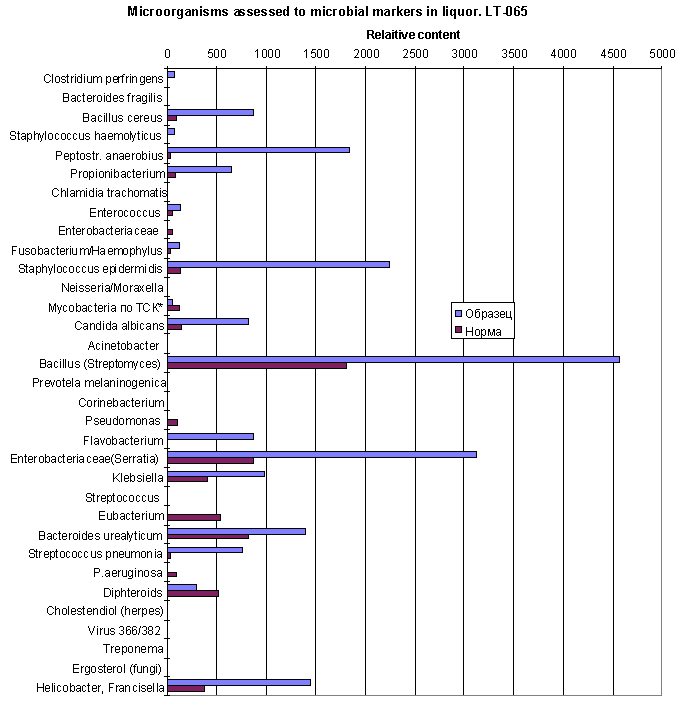
BEFORE TREATING
Microflora composition differ against normal in excess of Bacillus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Peptostreptococcus anaerobius, Streptococcus pneumonia, Enterobacteriaceae sps., Propionibacterium, Clostridium perfringens, Candida albicans and others, and also occurance of Flavobacterium. Exceed of hydroxyhexadecanoic and hydroxyoctadecanoic acids could be assessed also to Bacteroides and Helicobacter (items 24,33) as compared to Example 1. But Francisella could be suspected too.
2. After treating with diflucan
|
¹ |
Genera, species |
Sample content* |
Normal level** |
|
1 |
Clostridium perfringens |
61 |
10 |
|
2 |
Bacteroides fragilis |
0 |
2 |
|
3 |
Bacillus cereus |
0 |
83 |
|
4 |
Staphylococcus haemolyticus |
248 |
13 |
|
5 |
Peptostr. anaerobius |
1491 |
19 |
|
6 |
Propionibacterium |
389 |
71 |
|
7 |
Chlamidia trachomatis |
0 |
1 |
|
8 |
Enterococcus |
0 |
50 |
|
9 |
Enterobacteriaceae |
0 |
56 |
|
10 |
Fusobacterium/Haemophylus |
139 |
21 |
|
11 |
Staphylococcus epidermidis |
2296 |
125 |
|
12 |
Neisseria/Moraxella |
153 |
0 |
|
13 |
Mycobacteria (TSA) |
0 |
114 |
|
14 |
Candida albicans |
232 |
136 |
|
15 |
Acinetobacter |
0 |
8 |
|
16 |
Bacillus (Streptomyces) |
3017 |
1800 |
|
17 |
Prevotela melaninogenica |
0 |
0 |
|
18 |
Corinebacterium |
0 |
0 |
|
19 |
Pseudomonas |
0 |
96 |
|
20 |
Flavobacterium |
0 |
0 |
|
21 |
Enterobacteriaceae(Serratia) |
885 |
863 |
|
22 |
Klebsiella |
496 |
397 |
|
23 |
Streptococcus |
0 |
0 |
|
24 |
Eubacterium |
0 |
526 |
|
25 |
Bacteroides urealyticum |
1202 |
816 |
|
26 |
Streptococcus pneumonia |
114 |
27 |
|
27 |
P.aeruginosa |
64 |
84 |
|
28 |
Diphteroids |
646 |
512 |
|
29 |
Cholestendiol (herpes) |
0,0 |
0 |
|
30 |
Virus 366/382 |
0 |
0,3 |
|
31 |
Treponema |
0 |
0,21 |
|
32 |
Ergosterol (fungi) |
0 |
0 |
|
33 |
Helicobacter, Francisella |
1962 |
369 |
The same data in diagram form:
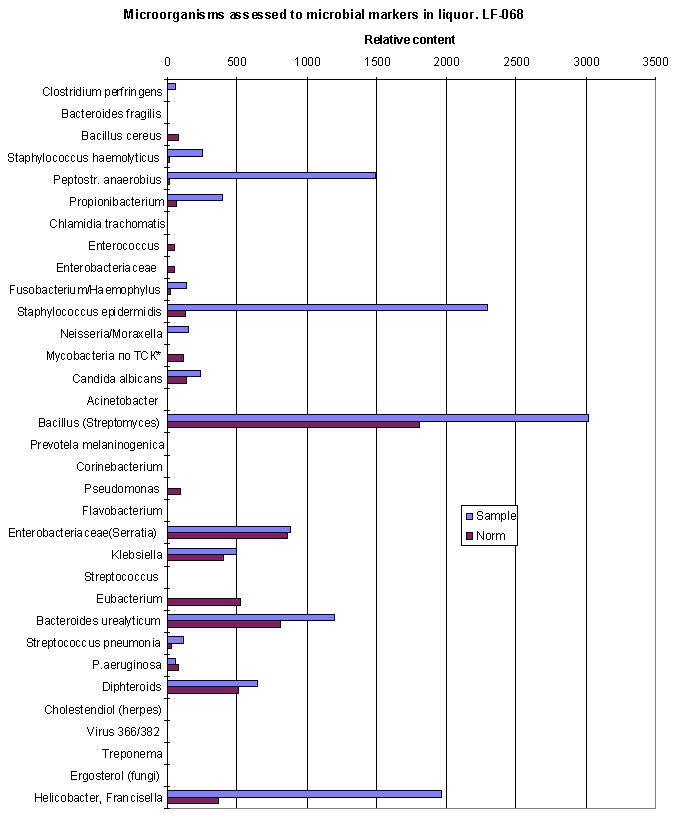
AFTER TREATING
As compared to previous analysis quantity of Enterobacteriaceae sps., , Candida albicans lowered to normal level. Flavobacterium was eradicated. Streptococcus pneumonia and Bacillus decreased, but still exceed norm., S.epidermidis, , Peptostreptococcus, Propionibacterium, Clostridium perfringens and Francisella remain prevalent.
Unfortunately, new pathogen, Moraxella was appeared.